At UPMC Sports Surgery Clinic, many of our Consultant Orthopedic Surgeons and Neurosurgeons use ExcelsiusGPS, a revolutionary robotic navigation platform designed to improve safety and accuracy in the operating room.
ExcelsiusGPS provides our surgeons with improved visualisation of a patient’s anatomy throughout the procedure, optimising patient treatment.
This revolutionary robotic navigation platform is the world’s first technology to combine a rigid robotic arm and full navigation capabilities into one adaptable platform for accurate trajectory alignment in spine surgery.
Robotic surgery may be considered a safer method than conventional spine surgery because it helps increase screw placement accuracy compared to conventional techniques.
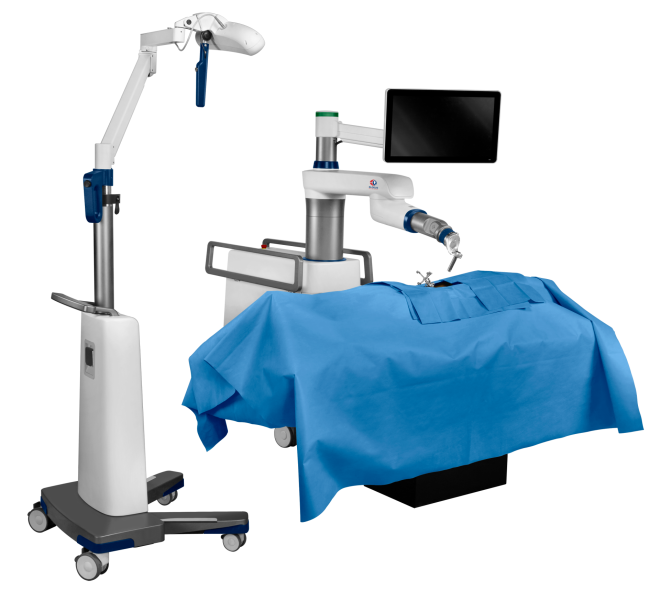
Robotic guidance provides assistance to your surgeon. The robotic arm aligns to a trajectory that is preplanned by your surgeon to help guide the surgeon’s placement of screw implants using surgical tools. Navigation is a way for your surgeon to see the surgical tools in relation to your body on a screen as they are being used.
What sets ExcelsiusGPS™ apart from other surgical robots is that surgeons can track patient movement on the table, allowing surgeons to make real-time adjustments during surgery to help ensure they stay on the pre-planned pathway.

No. The surgeon controls the surgical procedure 100% of the time. The robotic navigation system serves as an additional tool to help surgeons view and place screws according to their planned trajectory.
Spinal Surgeons and Neurosurgeons at UPMC Sports Surgery Clinic may utilise this robotic navigation system for a variety of spine procedures, including spinal fusion with posterior screw and rod fixation, transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF), lumbar lateral interbody fusion (LLIF), sacroiliac (SI) fusion, posterior cervical fixation, deformity correction, revision surgery, and more.
ExcelsiusGPS™ is designed to assist surgeons in cranial procedures by guiding cranial instruments according to the surgeon’s preplanned pathway during procedures such as shunt procedures, deep brain stimulation (DBS), biopsies, and stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG).
On the day of surgery, medical images are taken and imported into ExcelsiusGPS™. These images are used by your surgeon to determine the size and placement of implants and to create a surgical plan based on your anatomy. The surgical plan then guides the rigid robotic arm to the specific region where your surgery is planned, so the surgeon can place the screws at planned locations.
Recovery time varies between patients. Patients may notice improvement of some or all symptoms, and pain from surgery may diminish 2 to 4 weeks after surgery. The surgeon’s goal is for you to return to your normal activities as soon as possible. A positive attitude, reasonable expectations, and compliance with post-surgery instructions may contribute to a satisfactory outcome.













